Is it better to be small or large when the climate changes?
Large animals need a lot of space, and that is not always an advantage.
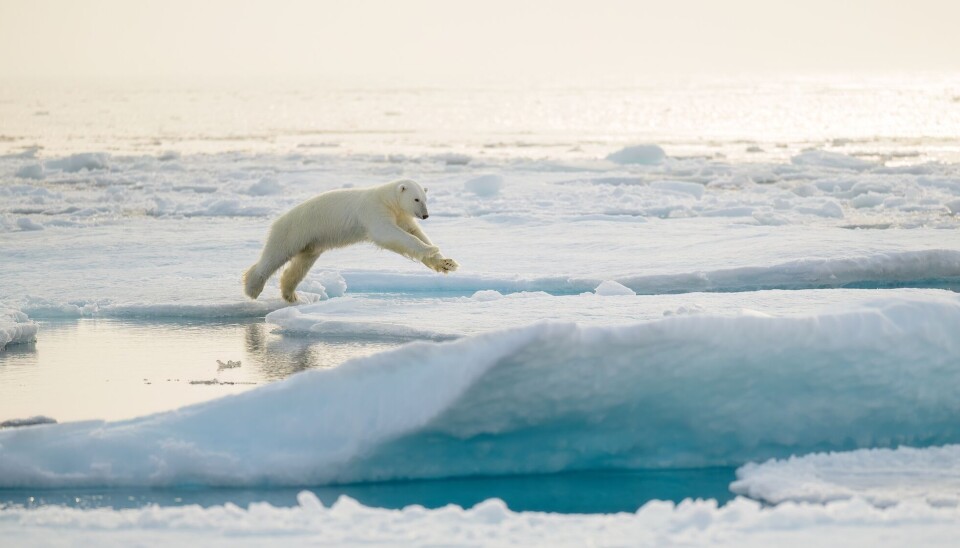

A large animal does not have many enemies, and if it does, it can often protect itself.
A small animal can be an easy target, but at the same time, it can be very good at hiding.
When the climate changes, many animals have to live a little differently than they do today. Is it then better to be small or large?
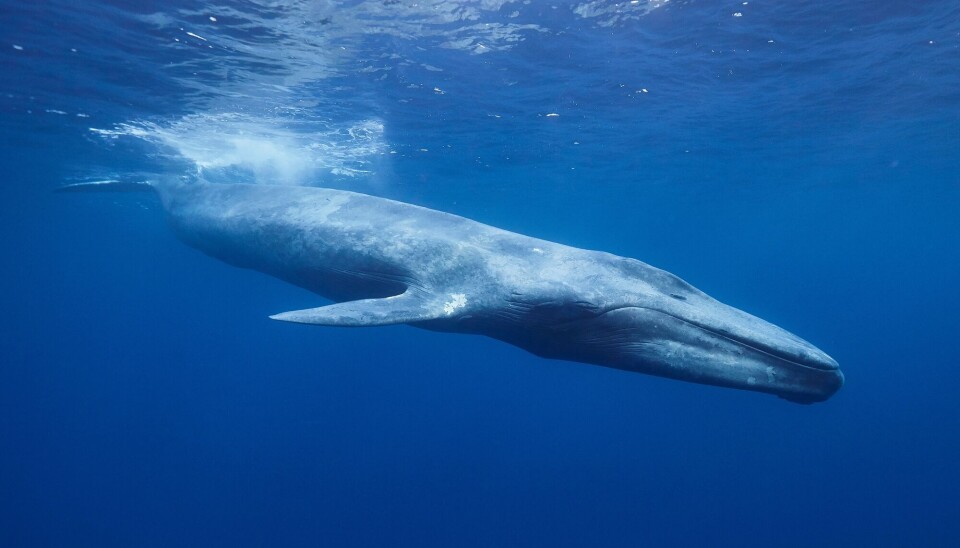

Needs a lot of space
When an animal is large, it naturally needs a lot of space.
"One reason some animals become extremely large is that they often face no resistance. A blue whale is so big that it's almost impossible for other animals to hunt it, except for humans," says Anette Högström.
She is a palaeontologist at UiT The Arctic University of Norway.
When nothing can hunt you, it becomes easier to grow large.
"This means that these animals require vast living spaces, and providing enough food demands significant resources. A blue whale cannot fit in a pool or a fjord. It's an animal that needs a lot of space to survive," she says.

As habitats shrink, this becomes a challenge for many large animals.
Many offspring
Large animals do not have many offspring, and there is a reason for that.
"Large animals use a lot of energy
to give birth to one or two young. They also invest a great deal of time and effort in taking care of them.
It takes a long time for their young to grow up, and they have longer lifespans. As a result, there are fewer individuals of the species," explains Högström.
When there are not many individuals of a species, there is a high risk of extinction if a disaster occurs.
This is not the case for small animals, as they can have many offspring.
Take the house mouse, for example. It can have five or six babies per litter and up to 14 litters in a single year.
"A mouse also requires less food and less space to live. If the climate changes, one of the many offspring may survive. That means this mouse has adapted to the new conditions and can pass on this knowledge to its own offspring," she says.
Prehistoric animals
"It's crucial to study what happened when many species disappeared in the past so we can better understand what affects different animals. It's difficult to pinpoint a single reason for extinction because many factors are involved," says Högström.
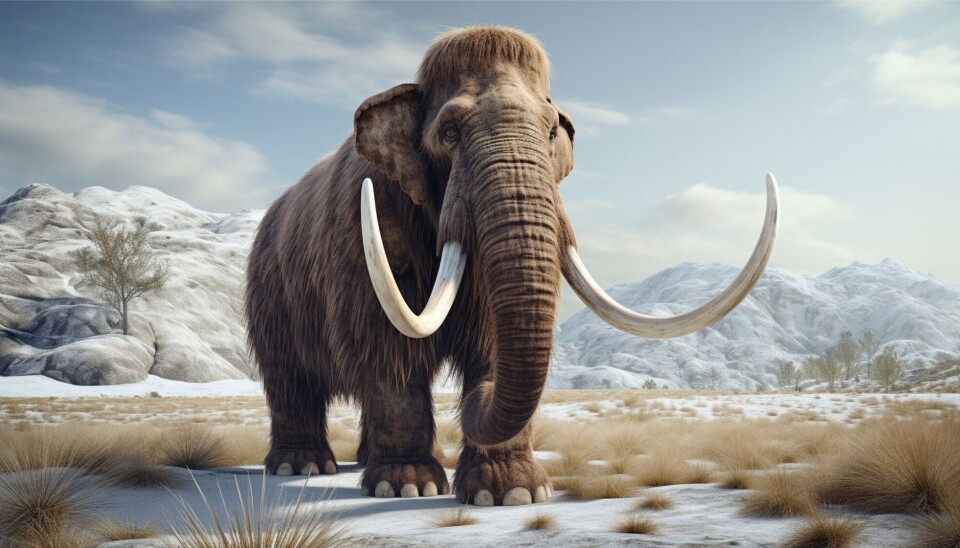

The mammoth is an example of a prehistoric animal that was affected by climate change.
Most viewed
"As the climate warmed, mammoths had less space and less food, making it harder for them to survive," she says.
Something similar is happening today with polar bears.
"The polar bear is adapted to a cold climate, so there are clear similarities between it and the mammoth. Humans have damaged the environment in various ways, leading to much warmer temperatures," she says.
Polar bears are also large animals that need a lot of space.
"The polar bear has one or two cubs every second or third year, and if they do not survive, it takes a long time before there are more adult polar bears. If three to four years pass with cubs that do not survive, the chances of the species surviving decrease," says Högström.
———
Translated by Alette Bjordal Gjellesvik
Read the Norwegian version of this article on ung.forskning.no
References:
Britannica: Blue whales, elephants, house mice, polar bears
Related content:
Subscribe to our newsletter
The latest news from Science Norway, sent twice a week and completely free.

























































